The 4C's diamonds
The 4C's are the key used to evaluate lab grown diamonds. The Carat measures the mass of the diamond, while the Clarity assesses the presence of inclusions or imperfections. Color examines the hue of the diamond, ranging from colorless to more pronounced shades of color. Cut refers to proportion, symmetry and polish, which affects the brilliance and sparkle of the diamond. Together, these criteria provide a comprehensive assessment of the quality and value of lab grown diamonds
CARAT
CARAT is a unit of measurement for expressing the weight of diamonds and precious stones. Its abbreviation is ct. Carat weight is one of the most important characteristics in determining the value of a diamond. One carat is equal to 0.2 grams, 200 milligrams and can be divided into 100 points. Diamonds weighing less than one carat can be expressed in points, for a diamond of 0.55 carat we will speak of a “55 points”.
1 carat = 0.2 g = 200 mg = 100 points.
The value of a lab grown diamond increases exponentially with its weight, so a 3 carat diamond is worth more than three diamonds, of equal quality, of 1 carat. This explains the weight thresholds beyond which the price of diamonds increases significantly. 0.50 ct 1ct 1.50ct 2cts so a 0.97 ct diamond is significantly less expensive than a 1 carat diamond. lab grown diamonds of different shapes such as rectangle, square or oval can be visually larger or smaller for the same carat weight.
The little history of the carat:
Carob seeds are the origin of the carat in fact they have the particularity of having a very constant weight of approximately 0.197 grams and were very early used as a unit of weight. In 1907, the metric carat of 0.2 grams was adopted and is universally used today.
COLOR
The majority of lab grown diamonds vary in color from colorless to yellow or light brown. They belong to the Cape series. A color scale graduated from the Letter D (the most colorless) to the letter Z (yellow to light brown) allows you to determine the color. This assessment, carried out in the laboratory by comparison with standard stones, has become an international and essential standard for the diamond market in general.
If a lab grown diamond composed solely of carbon is colorless, it may contain atomic impurities or structural defects; these anomalies then become chromogenic centers which will color the stone. The vast majority of lab grown diamonds are type IIA, the highest distinction among colorless diamonds, meaning they contain neither nitrogen nor boron.
likely to nuance their perfectly pure “water”. Lab grown diamonds also come in all the colors of the rainbow, yellow, pink, blue... they are called Fancy Colors in English; their shade is clear and evaluated using a different color scale.
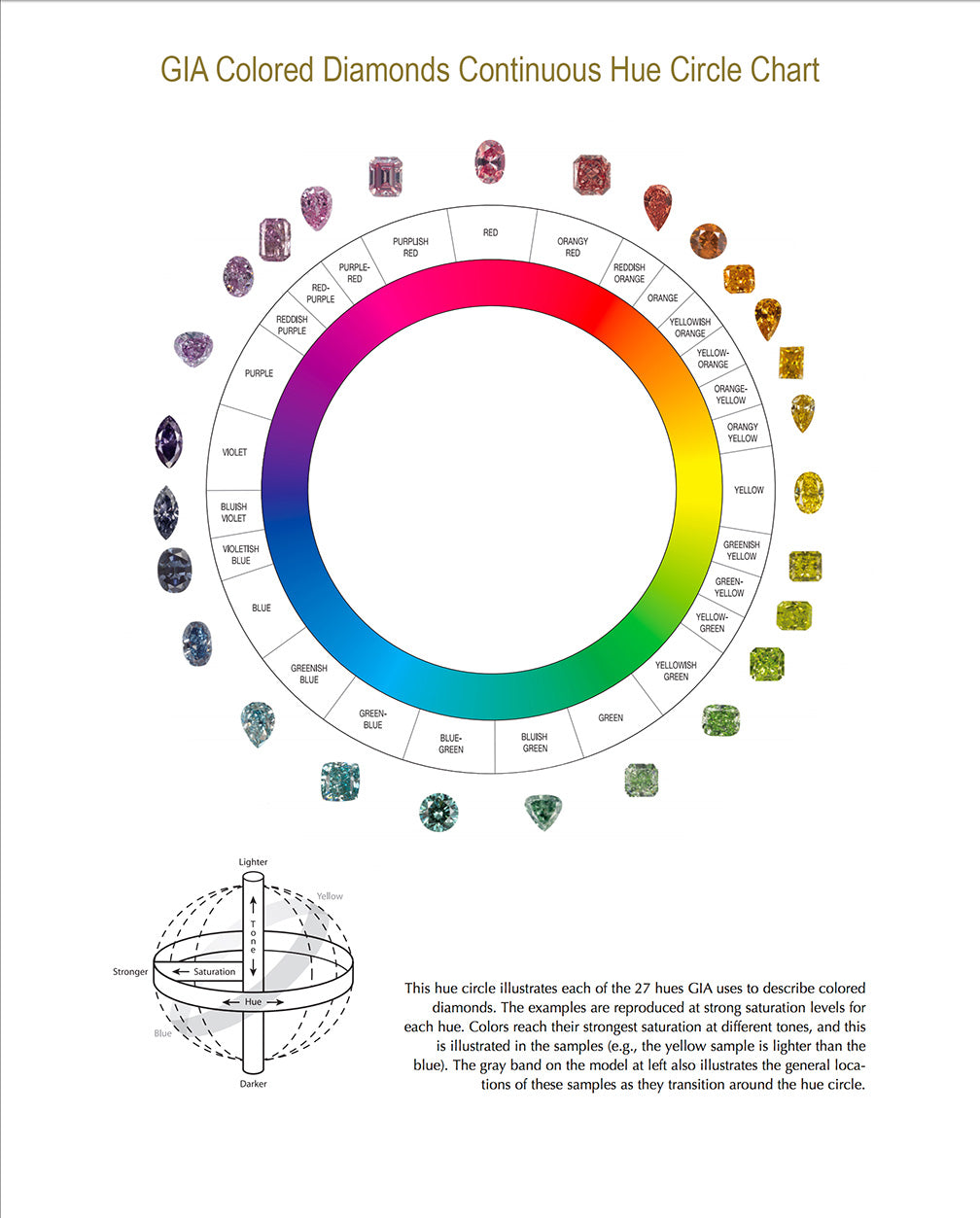
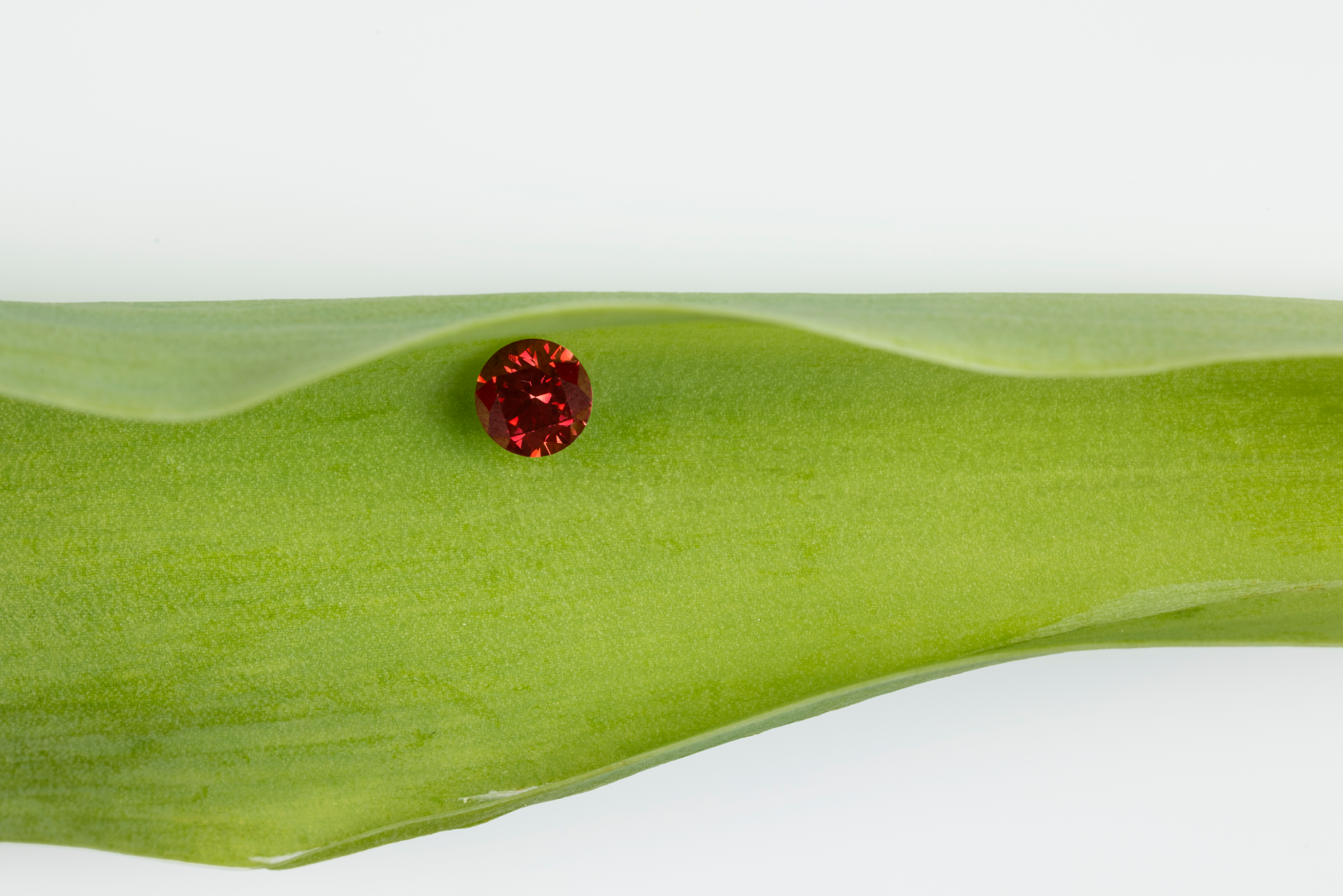
FANCY COLOR LAB DIAMONDS
Fancy colors Lab Grown Diamonds
If Lab gron diamonds are known for their color
white to colorless from the Cape series, they also exist in all the colors of the rainbow. These bold and attractive colors make them increasingly sought after in the world of jewelry, in English they are called Fancy colors. Immersion in color is a magical world, where each stone changes tone depending on the lighting and according to the unique perception of each person.
Atomic impurities or structural defects are at the origin of the most particular colors. Unlike round and colorless lab grown diamonds, original shapes such as cushion, oval, pear, etc. increase the intensity of a color and therefore its value. The approach to reading gemmological certificates must be different for colored synthetic diamonds. Indeed if the evaluation is based on the analysis of the 4C's: Carat Color Clarity & Cut, the consideration of color will take on its full importance while the aspects of cut and Clarity will become very secondary.
Three criteria will define the color: the dominant color, its nuances and its graduated intensity from Fancy Light to Fancy Deep. The color of the fancy colors is given in English in this order:
[Fancy] [Intensity] [Shade 1] [dominant color]
FANCY DEEP GREENISH BLUE
CLARITY
Clarity assesses the presence of internal and external imperfections in a synthetic diamond.
The assessment is based on the significance of inclusions or imperfections. It takes into account their size, intensity, reflections within the stone, and finally their position. Clarity is graded on a scale ranging from "Flawless" to "Included." A diamond with high clarity has fewer imperfections, which increases its value.
CUT
The cut of a lab grown diamond directly refers to its brilliance and fire. This manual intervention by man on the stone depends on the talent of the cutter and his know-how.
Cut is the combination of three aspects: proportion, symmetry and polish. All three are graded on your gemology certificate on the grading scale
following: Excellent – Very Good – Good – Fair.
They will determine on the one hand the brilliance of the diamond, that is to say the external and internal reflection of the light rays and on the other hand the lights of the diamond, that is to say the splitting of a light ray in the colors of the rainbow.
Hearts & Arrows round lab grown diamonds have the visual particularity of revealing heart motifs seen through the crown and arrows seen through the pavilion. They are the result of a symmetry to the strictest standards.